Building Cloud Expertise with centron - Our Tutorials
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, our practical tutorials provide you with the knowledge you need to make the most of our cloud services.
Spring Restful Web Services Example
Spring is one of the most widely used Java EE frameworks. We have earlier seen how to use Spring MVC to create Java-based web applications. Today we will learn to create Spring Restful Web Services using Spring MVC and then test it out with the Rest client. In the end, we will also look into how to invoke Spring Restful web service using Spring RestTemplate API.
Spring REST
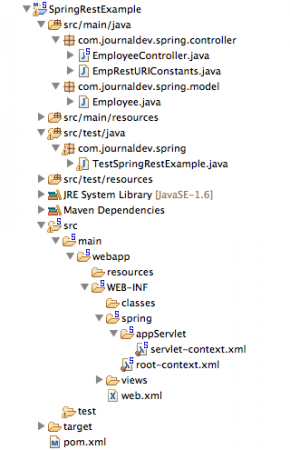
We will use Spring latest version 4.0.0.RELEASE and utilize Spring Jackson JSON integration to send JSON response in the rest call response. The tutorial is developed in Spring STS IDE for creating Spring MVC skeleton code easily and then extended to implement Restful architecture. Create a new Spring MVC Project in the STS, our final project will look like the below image. We will look into each of the components one by one.
Spring REST Configuration XML Files
Our pom.xml file looks like below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.journaldev</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringRestExample</artifactId>
<name>SpringRestExample</name>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0.0-BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java-version>1.6</java-version>
<org.springframework-version>4.0.0.RELEASE</org.springframework-version>
<org.aspectj-version>1.7.4</org.aspectj-version>
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.5</org.slf4j-version>
<jackson.databind-version>2.2.3</jackson.databind-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.databind-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- Exclude Commons Logging in favor of SLF4j -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${org.aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>mail</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.jms</groupId>
<artifactId>jms</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jdmk</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxtools</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.sun.jmx</groupId>
<artifactId>jmxri</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- @Inject -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.7</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
<configuration>
<additionalProjectnatures>
<projectnature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</projectnature>
</additionalProjectnatures>
<additionalBuildcommands>
<buildcommand>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springbuilder</buildcommand>
</additionalBuildcommands>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
<compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
<compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>org.test.int1.Main</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
STS tool generates the pom.xml file for us. However, I have updated the Spring Framework, AspectJ, SLF4J and Jackson version to the latest one as of today. Most of the part is common and generated automatically, the important point to note is that I have added Jackson JSON libraries in the dependency because we will use that to convert Objects to JSON and vice versa.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5" xmlns="https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee https://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<!-- The definition of the Root Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Creates the Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Processes application requests -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
This file is generated automatically and I haven’t changed anything in that. However, if you want to change context configuration files and their location, you can do it in the web.xml file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- Root Context: defines shared resources visible to all other web components -->
</beans>
This file contains the shared resources that will be visible to all the web components, we will be developing a simple rest service and that’s why I haven’t changed anything here.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:beans="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<!-- Handles HTTP GET requests for /resources/** by efficiently serving up static resources in the ${webappRoot}/resources directory -->
<resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
<!-- Configure to plugin JSON as request and response in method handler -->
<beans:bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<beans:property name="messageConverters">
<beans:list>
<beans:ref bean="jsonMessageConverter"/>
</beans:list>
</beans:property>
</beans:bean>
<!-- Configure bean to convert JSON to POJO and vice versa -->
<beans:bean id="jsonMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
</beans:bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.journaldev.spring.controller" />
</beans:beans>
Most of the part is auto generated and contains boiler-plate configurations. However important points to note are annotation-driven element to support annotations based configuration and plugging in MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter to the RequestMappingHandlerAdapter messageConverters so that Jackson API kicks in and converts JSON to Java Beans and vice versa. By having this configuration, we will be using JSON in request body and we will receive JSON data in the response.
Spring REST Model Classes
Let’s write a simple POJO class that will serve as input and output to our Restful web service methods.
package com.journaldev.spring.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.DateSerializer;
public class Employee implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7788619177798333712L;
private int id;
private String name;
private Date createdDate;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@JsonSerialize(using=DateSerializer.class)
public Date getCreatedDate() {
return createdDate;
}
public void setCreatedDate(Date createdDate) {
this.createdDate = createdDate;
}
}
The only important point to note is the use of @JsonSerialize annotation to use DateSerializer class for Date conversion from Java type to JSON format and vice versa.
Spring Restful Web Service Endpoints
We will have the following rest web services endpoints.
| Sl. No | URI | HTTP Method | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
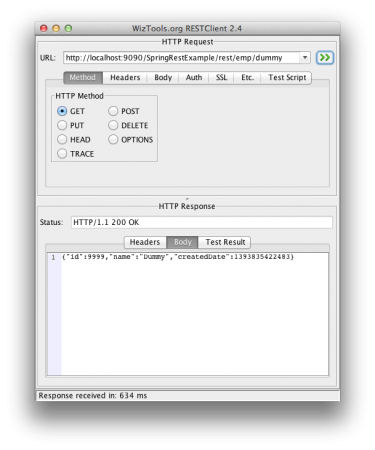
| 1 | /rest/emp/dummy | GET | Health Check service, to insert a dummy data in the Employees data storage |
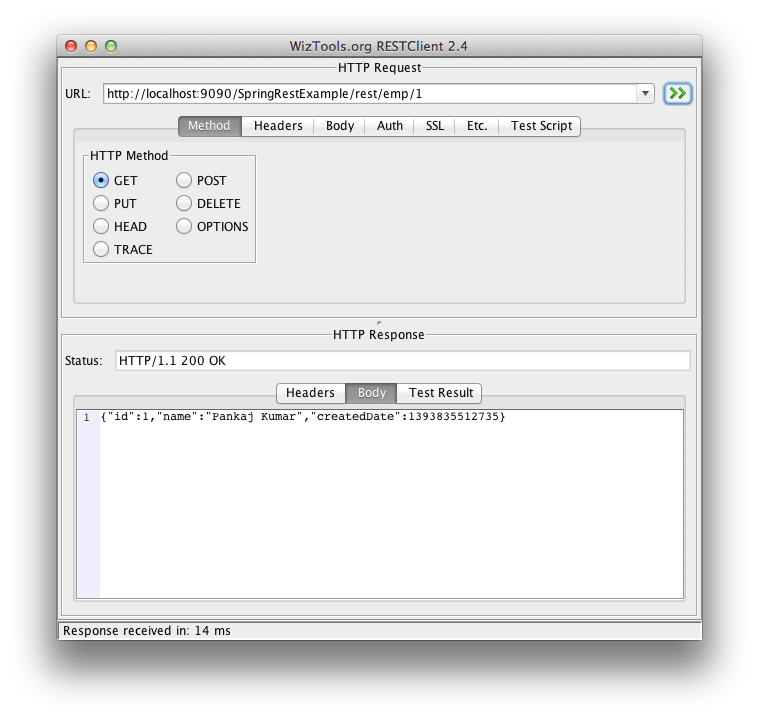
| 2 | /rest/emp/{id} | GET | To get the Employee object based on the id |
| 3 | /rest/emps | GET | To get the list of all the Employees in the data store |
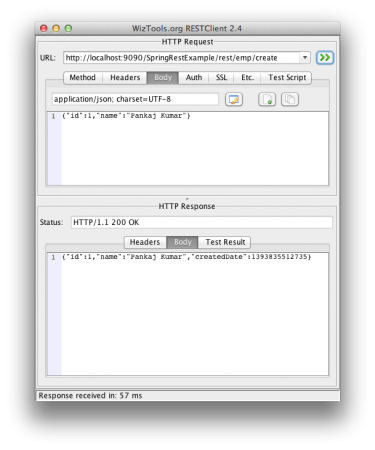
| 4 | /rest/emp/create | POST | To create the Employee object and store it |
| 5 | /rest/emp/delete/{id} | PUT | To delete the Employee object from the data storage based on the id |
We have a class defining all these URI as String constants.
package com.journaldev.spring.controller;
public class EmpRestURIConstants {
public static final String DUMMY_EMP = "/rest/emp/dummy";
public static final String GET_EMP = "/rest/emp/{id}";
public static final String GET_ALL_EMP = "/rest/emps";
public static final String CREATE_EMP = "/rest/emp/create";
public static final String DELETE_EMP = "/rest/emp/delete/{id}";
}
Spring Restful web service Controller class
Our EmployeeController class will publish all the web service endpoints mentioned above. Let’s look at the code of the class and then we will learn about each of the methods in detail.
package com.journaldev.spring.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee;
/**
* Handles requests for the Employee service.
*/
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmployeeController.class);
//Map to store employees, ideally we should use database
Map<Integer, Employee> empData = new HashMap<Integer, Employee>();
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.DUMMY_EMP, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody Employee getDummyEmployee() {
logger.info("Start getDummyEmployee");
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setId(9999);
emp.setName("Dummy");
emp.setCreatedDate(new Date());
empData.put(9999, emp);
return emp;
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.GET_EMP, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") int empId) {
logger.info("Start getEmployee. ID="+empId);
return empData.get(empId);
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.GET_ALL_EMP, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody List getAllEmployees() {
logger.info("Start getAllEmployees.");
List emps = new ArrayList();
Set empIdKeys = empData.keySet();
for(Integer i : empIdKeys){
emps.add(empData.get(i));
}
return emps;
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.CREATE_EMP, method = RequestMethod.POST)
public @ResponseBody Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
logger.info("Start createEmployee.");
emp.setCreatedDate(new Date());
empData.put(emp.getId(), emp);
return emp;
}
@RequestMapping(value = EmpRestURIConstants.DELETE_EMP, method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public @ResponseBody Employee deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("id") int empId) {
logger.info("Start deleteEmployee.");
Employee emp = empData.get(empId);
empData.remove(empId);
return emp;
}
}
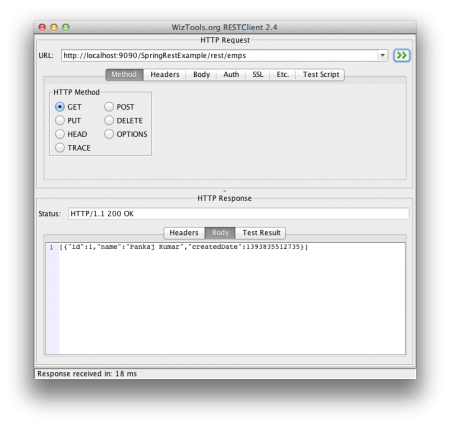
For simplicity, I am storing all the employee’s data in the HashMap empData. … Rest of the code is simple and self-understood, our application is ready for deployment and testing. … Below screenshots shows the different invocations of the rest APIs exposed by our application and it’s output.
Create Employee POST Rest Call: Make sure request Content-Type is set to “application/json” otherwise you will get HTTP Error Code 415.
Get Employee Rest Call
Delete Employee Rest Call
Get All Employees Rest Call
Spring Rest Client Program
Rest Clients are good to test our rest web service but most of the times, we need to invoke rest services through our program. We can use Spring RestTemplate to invoke these methods easily. Below is a simple program invoking our application rest methods using RestTemplate API.
package com.journaldev.spring;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.journaldev.spring.controller.EmpRestURIConstants;
import com.journaldev.spring.model.Employee;
public class TestSpringRestExample {
public static final String SERVER_URI = "https://localhost:9090/SpringRestExample";
public static void main(String args[]){
testGetDummyEmployee();
System.out.println("*****");
testCreateEmployee();
System.out.println("*****");
testGetEmployee();
System.out.println("*****");
testGetAllEmployee();
}
private static void testGetAllEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
//we can't get List because JSON convertor doesn't know the type of
//object in the list and hence convert it to default JSON object type LinkedHashMap
List emps = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVER_URI+EmpRestURIConstants.GET_ALL_EMP, List.class);
System.out.println(emps.size());
for(LinkedHashMap map : emps){
System.out.println("ID="+map.get("id")+",Name="+map.get("name")+",CreatedDate="+map.get("createdDate"));;
}
}
private static void testCreateEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setId(1);emp.setName("Pankaj Kumar");
Employee response = restTemplate.postForObject(SERVER_URI+EmpRestURIConstants.CREATE_EMP, emp, Employee.class);
printEmpData(response);
}
private static void testGetEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
Employee emp = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVER_URI+"/rest/emp/1", Employee.class);
printEmpData(emp);
}
private static void testGetDummyEmployee() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
Employee emp = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVER_URI+EmpRestURIConstants.DUMMY_EMP, Employee.class);
printEmpData(emp);
}
public static void printEmpData(Employee emp){
System.out.println("ID="+emp.getId()+",Name="+emp.getName()+",CreatedDate="+emp.getCreatedDate());
}
}
Most of the program is simple to understand, however when invoking rest method returning a Collection, we need to use LinkedHashMap because JSON to object conversion doesn’t know about the Employee object and converts it to the collection of LinkedHashMap. We can write a utility method to convert from LinkedHashMap to our Java Bean object. When we run the above program, we get the following output in the console.
ID=9999,Name=Dummy,CreatedDate=Tue Mar 04 21:02:41 PST 2014
*****
ID=1,Name=Pankaj Kumar,CreatedDate=Tue Mar 04 21:02:41 PST 2014
*****
ID=1,Name=Pankaj Kumar,CreatedDate=Tue Mar 04 21:02:41 PST 2014
*****
2
ID=1,Name=Pankaj Kumar,CreatedDate=1393995761654
ID=9999,Name=Dummy,CreatedDate=1393995761381
Another point is that RestTemplate put methods doesn’t have option to set response object because PUT method should be used to store something on the server and a simple HTTP 200 status code should be sufficient.
That’s all for the Spring Restful web application tutorial.
Create a Free Account
Register now and gain exclusive access to advanced resources, personalized support, and a community of experts.
Recent posts
Start Your Free Trial: Unleash the Power of Spring Restful Web Services in the Cloud!
Dive into the world of cloud-based solutions with our Spring Restful Web Services. Our platform offers an intuitive, scalable environment tailor-made for developing and managing your APIs with ease.